Proximity Sensor via Ultrasonic Sonar Module: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| (16 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Part of the [[Sensors_and_Controls_@_DILC|Sensors and Controls Project]], this Arduino micro-based Proximity Sensor integrates | Part of the [[Sensors_and_Controls_@_DILC|Sensors and Controls Project]], this Arduino micro-based Proximity Sensor integrates an Ultrasonic Sonar module. With this, one can easily monitor if there's someone near or around a specific area, say, room, door, gate. | ||
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
I. '''OBJECTIVES''' | I. '''OBJECTIVES''' | ||
* To make an Arduino based Proximity sensor via Ultrasonic Sonar module | |||
* To make an Arduino-based Proximity sensor via Ultrasonic Sonar module | |||
* To simulate effectiveness by varying distances | * To simulate effectiveness by varying distances | ||
| Line 15: | Line 17: | ||
II. '''MATERIALS & COMPONENTS''' | II. '''MATERIALS & COMPONENTS''' | ||
* Arduino micro/ Arduino UNO | * Arduino micro/ Arduino UNO | ||
[[File:ARDUINO_UNO.png| | [[File:ARDUINO_UNO.png|300px]] [[File:ARDUINO_MICRO.jpg|300px]] | ||
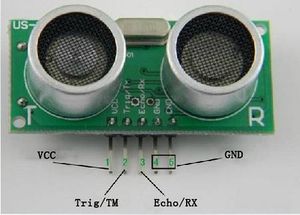
* Ultrasonic Sonar Module (US-100) | * Ultrasonic Sonar Module (US-100) | ||
[[File:SENSOR.jpg| | [[File:SENSOR.jpg|300px]] | ||
* Jumper wires | * Jumper wires | ||
[[File:JUMP_WIRE.jpg| | [[File:JUMP_WIRE.jpg|300px]] | ||
* 5 (Light Emitting Diodes) LEDs | * 5 (Light Emitting Diodes) LEDs | ||
[[File:5_LED.jpg| | [[File:5_LED.jpg|300px]] | ||
* 6 330K ohms Resistors | * 6 330K ohms Resistors | ||
[[File:RESISTORS.jpg| | [[File:RESISTORS.jpg|300px]] | ||
* Piezo Buzzer | * Piezo Buzzer | ||
[[File:PIEZO_BUZZER.jpg| | [[File:PIEZO_BUZZER.jpg|300px]] | ||
* Computer (with Arduino 1.0.5 Software) | * Computer (with Arduino 1.0.5 Software) | ||
[[File:ARDUINO.jpg| | [[File:ARDUINO.jpg|300px]] | ||
| Line 56: | Line 59: | ||
III. '''PROCEDURES''' | III. '''PROCEDURES''' | ||
1. Prepare all the materials. | 1. Prepare all the materials. | ||
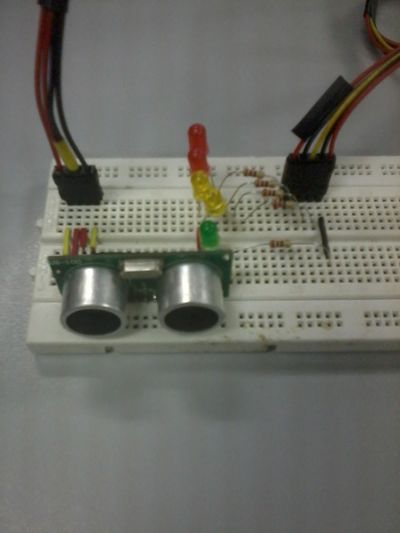
2. Put the corresponding components onto the breadboard. Make sure that the pins of the components are properly mounted to ensure the efficiency of the circuit. | |||
3. There are 5 pins of the US-100. From the back facing yourself, the 2 pins from the left are '''GROUND'''. The third pin from the left is the '''ECHO''', followed by the '''TRIGGER''' and lastly, the rightmost one, the '''VCC''' or the power. | |||
[[File:US100_BACK.jpg|200px]] [[File:US_100_FRONT.jpg|300px]] | |||
4. Connect the TRIGGER pin to '''Pin 6''' of the Arduino. Connect the ECHO pin to '''Pin 7''' of the Arduino. Make a connection between the 2 GROUND pins and connect it to '''GROUND pin''' of the Arduino. Also connect the VCC or power to the '''5V pin''' of the Arduino. | |||
[[File:PINNINGS.jpg|400px]] | |||
5. For indication purposes, you will connect 3 LEDs and a small buzzer. The GROUND pins of the LEDs and piezo buzzer will be connected to the GROUND pin of the US-100. The ANODE pins of LED1 to '''pin 8''', LED2 to '''pin 9''', LED3 to '''pin 10''', LED4 to '''pin11''' and LED5 to '''pin12'''. | |||
6. Have the code for the given circuit, use the Arduino 1.0.5 to program the operation of the circuit. See the code below and just copy and paste it on the Arduino 1.0.5. | |||
[[File:Code_for_Proximity_-_Google_Docs.pdf]] | |||
7. Verify the code that you program. Once done, upload the code to the Arduino and you can now test the capabilities of the proximity sensor. | |||
8. IF you want it to be used as a device, put it on a pcb, solder it and have a suitable casing for it. With this, you can prolong the life of the device and it will be more portable and efficient. | |||
| Line 75: | Line 95: | ||
IV. '''SIMULATION''' | IV. '''SIMULATION''' | ||
As soon as you upload the code on the arduino, it will take seconds for the sensor to be working efficiently. | |||
* When something blocks and is greater than 3 meter range, the LEDs will not light up. | |||
[[File:FinalTest1.jpg|300px]] | |||
* When something blocks and is within the range of 2.51 to 3 meters, the GREEN light will turn on. | |||
[[File:FinalTest2.jpg|300px]] | |||
* When something blocks and is within the range of 2.1 to 2.5 meters, the GREEN light and one YELLOW light will light up. | |||
[[File:FinalTest3.jpg|300px]] | |||
* When something blocks and is within the range of 1.51 to 2 meters, the GREEN light, and the 2 YELLOW lights will light up. | |||
[[File:FinalTest4.jpg|300px]] | |||
* When something blocks and is within the range of 1.1 to 1.5 meters, the GREEN light, the 2 YELLOW lights and one RED light will light up. | |||
[[File:FinalTest5.jpg|300px]] | |||
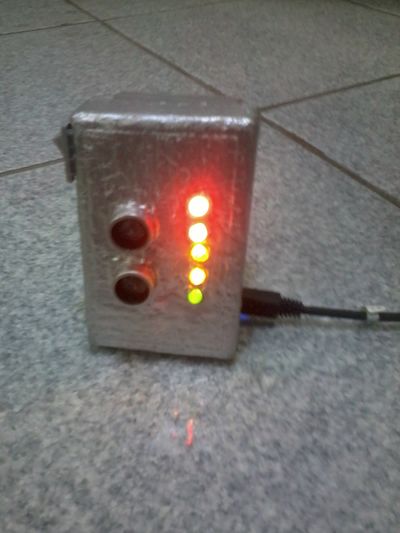
* When something blocks and is very near and within the range of 0 to 1 meter, ALL LEDs will light up. | |||
[[File:FinalTest6.jpg|300px]] | |||
For added alarm indicator, the LEDs were put into blinking. | |||
| Line 81: | Line 136: | ||
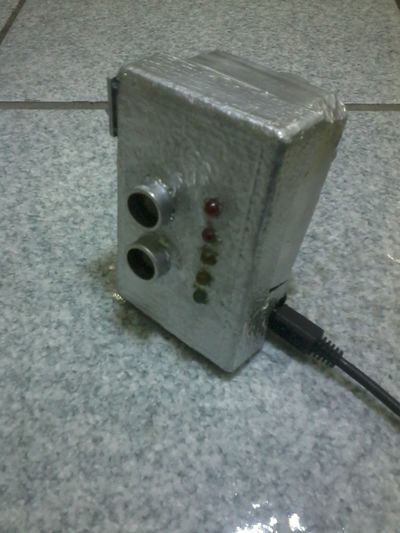
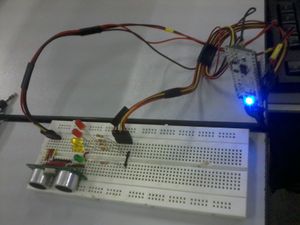
V. '''OTHER PHOTOS''' | V. '''OTHER PHOTOS''' | ||
[[File:Final1.jpg|400px]] | |||
[[File:Final2.jpg|400px]] | |||
'''Putting it on a PCB''' | |||
[[File:Pcb1.jpg|400px]] | |||
[[File:Pcb2.jpg|400px]] | |||
[[File:Pcb3.jpg|400px]] | |||
[[File:Pcb4.jpg|400px]] | |||
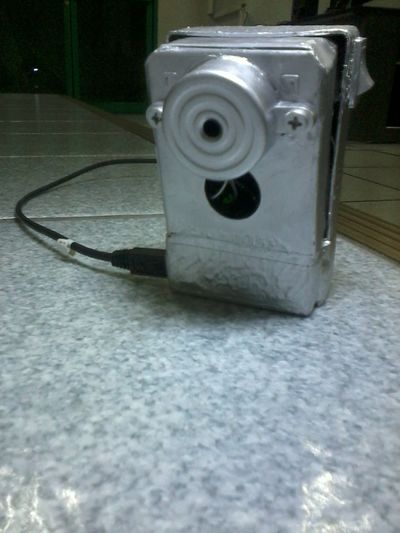
'''Proximity Sensor in a Casing''' | |||
''- for the safety and longevity of the device'' | |||
[[File:CASING1.jpg|400px]] | |||
[[File:CASING2.jpg|400px]] | |||
[[File:2014-05-20_10.28.15.jpg|400px]] | |||
[[File:2014-05-20_10.28.30.jpg|400px]] | |||
[[File:2014-05-20_10.28.57.jpg|400px]] | |||
[[File:2014-05-20_10.29.18.jpg|400px]] | |||
[[File:2014-05-20_10.31.46.jpg|400px]] | |||
[[Category:DILC Projects]] | |||
| Line 88: | Line 194: | ||
VI. '''REFERENCES''' | VI. '''REFERENCES''' | ||
[http://files.tested.com/photos/2013/06/12/48912-arduinouno_r3_front.jpg Arduino UNO Pin Configuration] | |||
[http://arduino.cc/en/Main/arduinoBoardMicro Arduino Micro Pin Configuration] | |||
[http://www.luntianlaboratory.com/code/us-100-distance-sensor/ Arduino Code] | |||
[https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7ZPc__5tL3c Video of How to setup the circuit] | |||
[http://randomnerdtutorials.com/arduino-ultrasonic-sensor-with-leds-and-buzzer/ Formation of the circuit] | |||
[http://www.generationrobots.com/en/content/65-ultrasonic-sonar-sensors-for-robots Literature about Ultrasonic sensor] | |||
---- | |||
==Development Team== | |||
* | |||
<br /><br /> | |||
[[Category:DILC Projects]] | [[Category:DILC Projects]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:28, 20 May 2014
Part of the Sensors and Controls Project, this Arduino micro-based Proximity Sensor integrates an Ultrasonic Sonar module. With this, one can easily monitor if there's someone near or around a specific area, say, room, door, gate.
I. OBJECTIVES
- To make an Arduino-based Proximity sensor via Ultrasonic Sonar module
- To simulate effectiveness by varying distances
II. MATERIALS & COMPONENTS
- Arduino micro/ Arduino UNO
- Ultrasonic Sonar Module (US-100)
- Jumper wires
- 5 (Light Emitting Diodes) LEDs
- 6 330K ohms Resistors
- Piezo Buzzer
- Computer (with Arduino 1.0.5 Software)
III. PROCEDURES
1. Prepare all the materials.
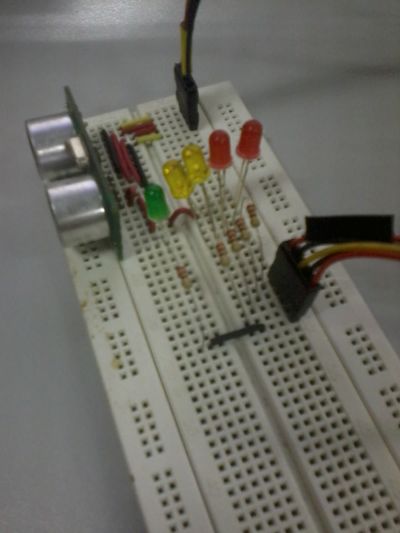
2. Put the corresponding components onto the breadboard. Make sure that the pins of the components are properly mounted to ensure the efficiency of the circuit.
3. There are 5 pins of the US-100. From the back facing yourself, the 2 pins from the left are GROUND. The third pin from the left is the ECHO, followed by the TRIGGER and lastly, the rightmost one, the VCC or the power.
4. Connect the TRIGGER pin to Pin 6 of the Arduino. Connect the ECHO pin to Pin 7 of the Arduino. Make a connection between the 2 GROUND pins and connect it to GROUND pin of the Arduino. Also connect the VCC or power to the 5V pin of the Arduino.
5. For indication purposes, you will connect 3 LEDs and a small buzzer. The GROUND pins of the LEDs and piezo buzzer will be connected to the GROUND pin of the US-100. The ANODE pins of LED1 to pin 8, LED2 to pin 9, LED3 to pin 10, LED4 to pin11 and LED5 to pin12.
6. Have the code for the given circuit, use the Arduino 1.0.5 to program the operation of the circuit. See the code below and just copy and paste it on the Arduino 1.0.5.
File:Code for Proximity - Google Docs.pdf
7. Verify the code that you program. Once done, upload the code to the Arduino and you can now test the capabilities of the proximity sensor.
8. IF you want it to be used as a device, put it on a pcb, solder it and have a suitable casing for it. With this, you can prolong the life of the device and it will be more portable and efficient.
IV. SIMULATION
As soon as you upload the code on the arduino, it will take seconds for the sensor to be working efficiently.
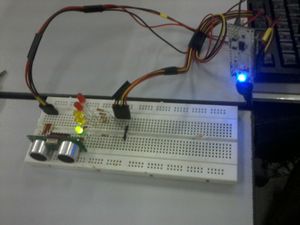
- When something blocks and is greater than 3 meter range, the LEDs will not light up.
- When something blocks and is within the range of 2.51 to 3 meters, the GREEN light will turn on.
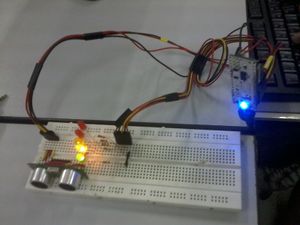
- When something blocks and is within the range of 2.1 to 2.5 meters, the GREEN light and one YELLOW light will light up.
- When something blocks and is within the range of 1.51 to 2 meters, the GREEN light, and the 2 YELLOW lights will light up.
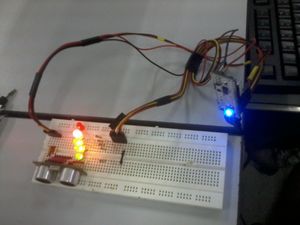
- When something blocks and is within the range of 1.1 to 1.5 meters, the GREEN light, the 2 YELLOW lights and one RED light will light up.
- When something blocks and is very near and within the range of 0 to 1 meter, ALL LEDs will light up.
For added alarm indicator, the LEDs were put into blinking.
V. OTHER PHOTOS
Putting it on a PCB
Proximity Sensor in a Casing
- for the safety and longevity of the device
VI. REFERENCES
Arduino Micro Pin Configuration
Video of How to setup the circuit
Literature about Ultrasonic sensor
Development Team